A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation. The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice. All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof the asset turnover ratio is calculated as net sales divided by should be guided accordingly. 11 Financial is a registered investment adviser located in Lufkin, Texas. 11 Financial may only transact business in those states in which it is registered, or qualifies for an exemption or exclusion from registration requirements. Finance Strategists has an advertising relationship with some of the companies included on this website.
How to Analyze Asset Turnover Ratio by Industry
- There are many other things involved in running a company such as cost, market share and brand name recognition.
- Lower ratios mean that the company isn’t using its assets efficiently and most likely have management or production problems.
- This ratio compares net sales displayed on the income statement to fixed assets on the balance sheet.
- The higher the asset turnover ratio, the better the company is performing, since higher ratios imply that the company is generating more revenue per dollar of assets.
- Manufacturing companies often favor the FAT ratio over the asset turnover ratio to determine how well capital investments perform.
- The fixed asset turnover ratio does not incorporate any company expenses.
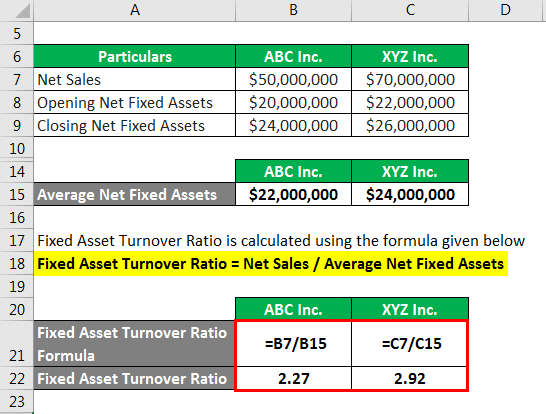
Similar to cash flow, the asset turnover ratio compares the company’s total assets over the course of a year to its sales. In simpler terms, it shows the dollar amount the company is earning in sales compared to the dollar amount of its assets. It can be calculated annually or over a shorter or longer period of time. FAT measures a company’s ability to generate net sales from its fixed-asset investments, namely property, plant, and equipment (PP&E). A higher fixed asset turnover ratio indicates that a company has effectively used investments in fixed assets to generate sales.
How to Improve Your Asset Turnover Ratio
In other words, this ratio shows how efficiently a company can use its assets to generate sales. In short, and to recap, asset turnover ratio looks at average total assets of a company — “total,” in this case, being the important qualifier. On the other hand, fixed asset turnover ratio looks at a company’s fixed assets to measure performance.
Asset Turnover Ratio: Formula, Examples, How to Improve It
To reach this number, you’ll need (unsurprisingly) two years of asset totals; you can find this information on your accounting balance sheet. Once you have your current year number and your previous number, add them up and divide them by two for the average. Instead, it gauges how efficiently a company utilizes its assets to generate sales. In the realm of financial analysis, the Asset Turnover Ratio plays a critical role. It provides significant insights into how efficiently a company uses its assets to generate sales.
XYZ has generated almost the same amount of income with over half the resources as ABC. Suppose company ABC had total revenues of $10 billion at the end of its fiscal year. Its total assets were $3 billion at the beginning of the fiscal year and $5 billion at the end. Assuming the company had no returns for the year, its net sales for the year were $10 billion. The company’s average total assets for the year was $4 billion (($3 billion + $5 billion) / 2 ). The asset turnover ratio is expressed as a rational number that may be a whole number or may include a decimal.
Limitations of the FAT
Asset turnover ratios vary across different industry sectors, so only the ratios of companies that are in the same sector should be compared. For example, retail or service sector companies have relatively small asset bases combined with high sales volume. Meanwhile, firms in sectors like utilities or manufacturing tend to have large asset bases, which translates to lower asset turnover. The asset turnover ratio uses the value of a company’s assets in the denominator of the formula.
Companies with cyclical sales may have low ratios in slow periods, so the ratio should be analyzed over several periods. Additionally, management may outsource production to reduce reliance on assets and improve its FAT ratio, while still struggling to maintain stable cash flows and other business fundamentals. Conversely, if a company has a low asset turnover ratio, it means it is not efficiently using its assets to create revenue. The asset turnover ratio is most useful when compared across similar companies. Due to the varying nature of different industries, it is most valuable when compared across companies within the same sector.
Check out our debt to asset ratio calculator and fixed asset turnover ratio calculator to understand more on this topic. A technology company like Meta has a significantly smaller fixed asset base than a manufacturing giant like Caterpillar. In this example, Caterpillar’s fixed asset turnover ratio is more relevant and should hold more weight for analysts than Meta’s FAT ratio. A higher turnover ratio indicates greater efficiency in managing fixed-asset investments. Analysts and investors often compare a company’s most recent ratio to historical ratios, ratio values from peer companies, or average ratios for the company’s industry.

